

trinucleotides or hexanucleotides), alterations in most regulatory regions (promoter regions) or deep intronic regions (greater than 20bp from an exon). This assay will not detect certain types of genomic alterations which may cause disease such as, but not limited to, translocations or inversions, repeat expansions (eg. The Schwartz-Jampel Syndrome (SJS) is a very rare condition characterised by Constant fndings such as typical facial appearance, muscle hypertrophy and. Its cardinal symptoms are skeletal dysplasia and neuromuscular hyperactivity. Definition: A syndrome characterized by neuromyotonia and chondrodysplasia that hasmaterialbasisin hypomorphic mutations in the HSPG2 gene on chromosome 1p36. Schwartz-Jampel syndrome (SJS) is a rare genetic disorder characterized by abnormalities of the skeletal muscles, including muscle weakness and stiffness. Identified putative deletions or duplications are confirmed by an orthogonal method (qPCR or MLPA). SchwartzJampel syndrome is a rare autosomal recessive disease with a prevalence of <1/10 6. If ordered, deletion/duplication analysis can identify alterations of genomic regions which include one whole gene (buccal swab specimens and whole blood specimens) and are two or more contiguous exons in size (whole blood specimens only) single exon deletions or duplications may occasionally be identified, but are not routinely detected by this test. Diagnosis is made by awareness into the typical phenotypic characters. Sanger sequencing is used to confirm variants with low quality scores and to meet coverage standards. Schwartz-Jampel syndrome is a very rare congenital myotonic syndrome with typical phenotypic and electrophysiological features. Although next generation sequencing technologies and our bioinformatics analysis significantly reduce the contribution of pseudogene sequences or other highly-homologous sequences, these may still occasionally interfere with the technical ability of the assay to identify pathogenic variant alleles in both sequencing and deletion/duplication analyses.
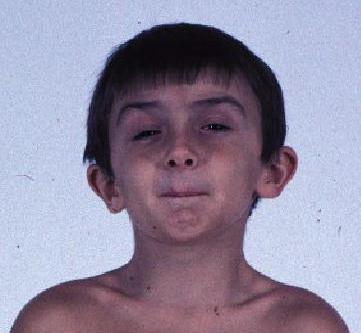
This analysis is performed by Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) and is designed to examine coding regions and splicing junctions. Schwartz-jampel Syndrome, Type 1 Sjs1 Is also known as sja syndrome, schwartz-jampel-aberfeld syndrome, sjs, myotonic myopathy, dwarfism, chondrodystrophy. SJS is primarily characterized by abnormalities of skeletal muscle, bone, and cartilage malformations of the eyes and the face and growth delays. Most people with SchwartzJampel syndrome have a nearly normal life expectancy. All sequencing technologies have limitations. Schwartz-Jampel syndrome type 1 (SJS type 1 ORPHA:800 OMIM255800) is a genetic disorder caused by a mutation of the HSPG2 gene. SchwartzJampel syndrome (SJS) is a rare genetic disease caused by a mutation in the perlecan gene (HSPG2) which causes osteochondrodysplasia associated with myotonia.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
